html
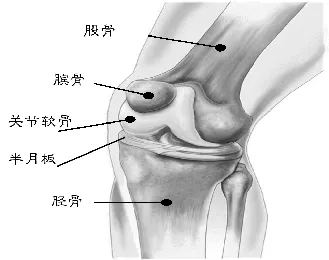
A Complete Guide to Knee Joint Protection: 8 Key Points for Daily Maintenance
One in four adults worldwide suffers from chronic knee pain. This precision “bearing” that bears 3-5 times the body weight every day, more than 90% of the damage comes from the wrong habits we are used to. Unlike other organs, cartilage tissue damage cannot be self-healed. This article will use data to reveal the 8 most common knee-injuring behaviors and provide scientific and effective solutions.
1. Sudden Long-Distance Walking

Real case: A 28-year-old white-collar worker tried to get fit by walking 20,000 steps a day, but after three days his knee was so swollen that he couldn’t bend it.
Mechanism of injury:
- When the leg muscles are not strong enough, gait control ability decreases by 27%
- Decreased knee joint stability leads to a 30% increase in cartilage impact
Correct way:
- Increase the number of steps per week by no more than 10%
- Keep the body’s centre of gravity vertical (imagine there is a string pulling from the top of your head)
- Keep your stride length at 50% of your height (about 85 cm for someone 170 cm tall)
- Use a pedometer to monitor your daily exercise
2. The Hidden Dangers of Jumping Rope on Concrete
Experimental data: The impact force generated on concrete is 2.3 times that on plastic.
Typical injuries:
- Patellar tendinitis (pain below the knee)
- Micro-fractures in the meniscus
Protective measures:
- Choose a wooden floor or a professional sports mat
- Wear air-cushioned running shoes (recommended forefoot-to-rearfoot drop ≤ 8mm)
- Land on the forefoot
- Do not jump rope for more than 15 minutes at a time
3. Risk of a Distorted Body-Jump
Common incorrect posture:
- Inverted knees when jumping (increases the pressure on the medial collateral ligament)
- Knee hyperextension on landing (causes injury to the posterior cruciate ligament)
Safe operating practices:
- No more than 15 reps per set
- Yoga mat thickness ≥ 6mm
- Wear patellar compression band
- Keep the torso parallel to the lower leg
4. Mechanics of Downhill Walking Injuries

Impact force formula: body weight (kg) × speed² × slope = pressure on the knee joint.
Typical data: A 60kg person walking down a 15° slope at 5km/h experiences a single-step impact force of 450kg.
Professional protection plan:
- Use hiking poles (22% impact reduction)
- Wear spring-loaded support knee pads
- Descend in a zigzag pattern
- Control downhill speed ≤ 3km/h
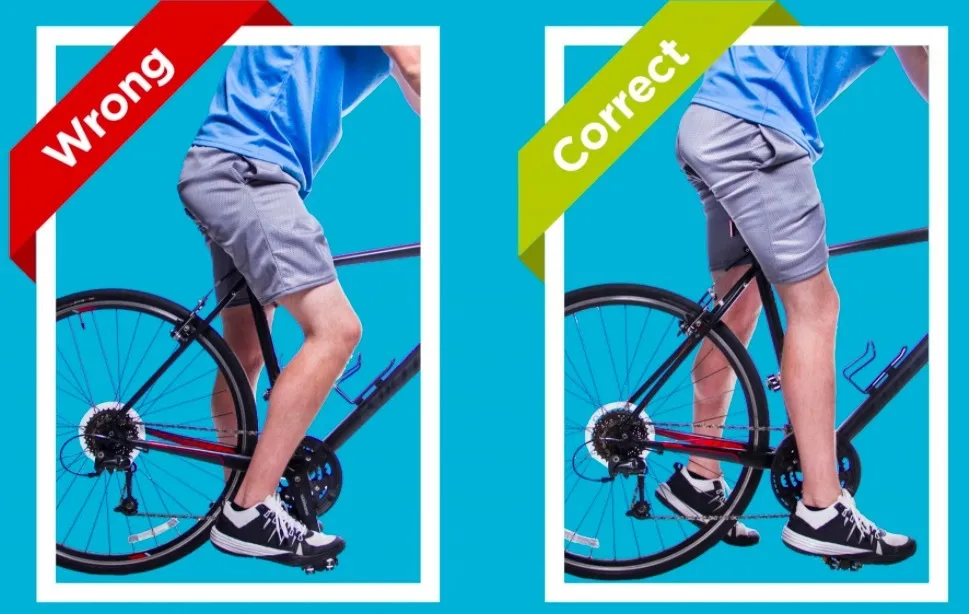
5. Sharing Bike Seat Adjustment

Golden formula for seat height: hip height – 2 cm = optimal seat height.
Consequences of incorrect adjustment:
- Too low causes knees to bend > 90°
- Too high causes knees to buckle
Adjustment tips:
- Heels should be able to rest fully on the pedal
- Knees should be bent 15-20° during normal riding
- Handlebar height should be flush with the seat
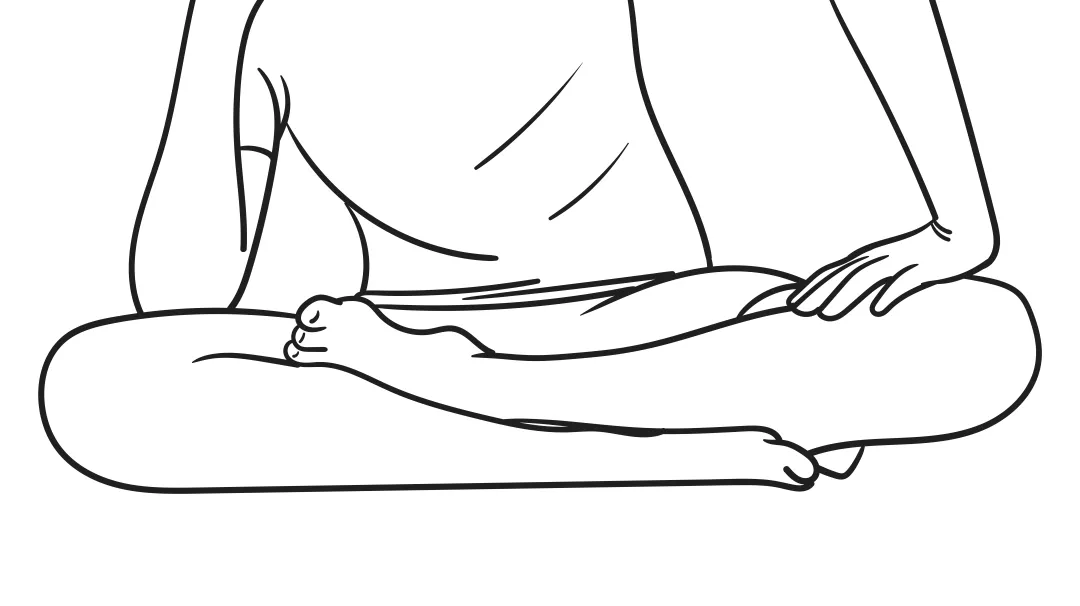
6. Potential Risks of Cross-Legged Sitting

Medical research shows: When the knee is bent more than 120°, the pressure on the meniscus increases threefold.
Recommendations for improving your sitting posture:
- Do not sit cross-legged for more than 15 minutes
- Use a 10 cm thick cushion
- Stretch your legs every 30 minutes
- Avoid kneeling
7. The Metabolic Crisis of Sedentary Lifestyles
Laboratory data:
- After 3 hours of continuous sitting, the synovial fluid in the joints decreases by 60%
- Cartilage nutrition supply decreases by 40%
Office micro-exercises (performed every hour):
- Seat squats: 5 times/set
- Resistance with elastic band: 20 times/set
- Toe tapping: 15 times/side
- Knee circles: 10 times clockwise/counterclockwise
8. The Hazards of Prolonged Squatting in the Toilet

Clinical statistics: Squatting for more than 5 minutes = 200 consecutive squats.
Scientific toilet solution:
- Use a 15 cm footrest to reduce the bending angle
- Maintain a sitting position on the toilet (knee bend < 90°)
- Control the time spent on the toilet < 3 minutes
- Seek medical attention if you have constipation problems
10-Minute Daily Maintenance Plan (Effective in 4 Weeks)

Movement 1: Static squats against the wall
- Back against the wall
- Bend your knees 90°
- Hold for 60 seconds × 3 sets
Movement 2: Elastic band training
- Place an elastic band around your ankle
- Move sideways for 15 steps
- 15 steps back and forth
- 3 sets per day
Movement 3: Single-leg balance
- Stand on one foot for 30 seconds
- Close eyes for added difficulty
- 3 times each to the left and right
- Use a padded mat for added difficulty
Post-exercise care:
- Ice for 15 minutes (separated by a towel)
- Use a compression bandage
- Raise your legs for 20 minutes
Long-Term Maintenance Strategy

- Check the wear of your sneakers every week
- Record daily knee condition (pain level, swelling level)
- Have a professional joint assessment every six months
- Keep BMI between 18.5 and 24
- Supplement with glucosamine and collagen (recommended after age 40)
Key Reminder

Seek medical attention immediately when the following symptoms appear:
- Morning stiffness that lasts more than two weeks
- Joints become hot and red
- Pain that worsens during the night
- Inability to complete a full squat
Scientific data shows that 90% of knee joint wear and tear comes from daily habits. Starting today, remember to adjust the seat height every time you sit down, and warm up before every exercise. These small changes will directly affect your mobility for the next 20 years. Remember: prevention is always more effective than treatment.
