“Unexpected glass breakage can turn daily routines into hazards—understand the science behind safe usage to protect your home and family.”
Introduction
Glass containers are trusted for their elegance and durability, but incidents like microwave explosions or spontaneous cracks raise valid concerns. This guide demystifies glass failure mechanisms while providing actionable safety strategies.
1. Why Do Glass Containers Break?
Breakage often stems from two factors: material type and usage patterns. Common glass varieties include:
- Soda-lime (everyday use)
- Tempered (safety glass)
- Borosilicate (lab-grade)
- Crystal (decorative)
Each type responds differently to thermal stress—the silent killer of glassware.
2. Types of Glass & Thermal Resistance
2.1 Soda-Lime Glass
Budget-friendly but fragile—resists just 50°C temperature changes. Avoid extreme heat transitions.
2.2 Tempered Glass
Heat-treated for strength, withstands 200°C temperature shocks. Breaks into safe pellets when damaged.
2.3 Borosilicate Glass
Scientifically engineered for 150°C thermal resistance. Safe for freezer-to-oven transitions.

2.4 Crystal Glass
Lead-enhanced clarity but poor heat tolerance—limit to 60°C temperature changes.
3. 4 Common Mistakes Causing Breakage
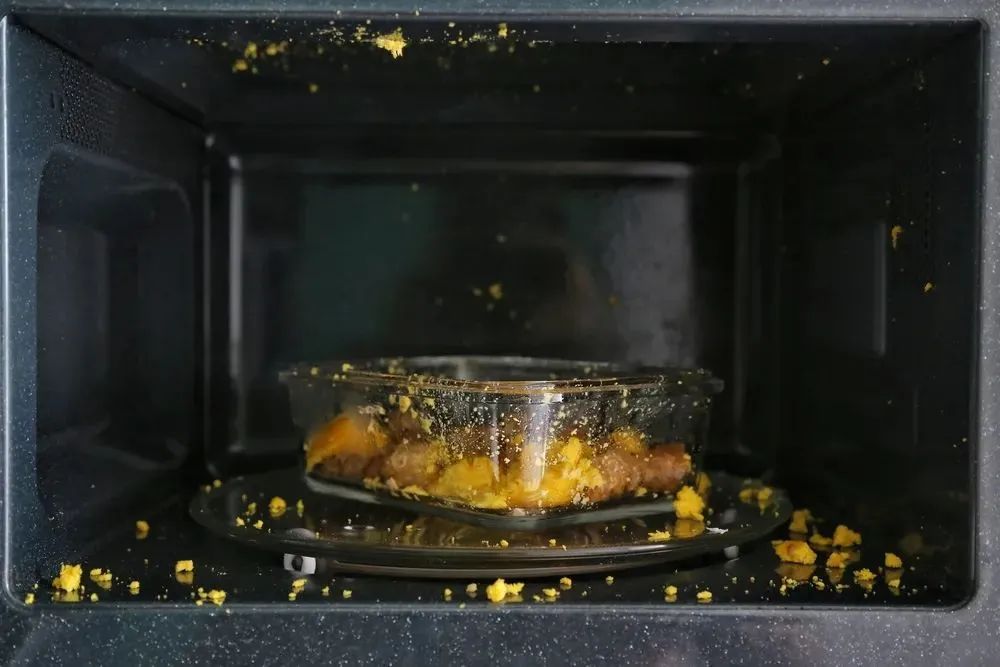
- Heating sealed containers (steam pressure buildup)
- Dry-heating bread/pasta (uneven thermal expansion)
- Using airtight lids (pressure cooker effect)
- Leaving metal utensils inside (microwave arcing)
4. Choosing Safe Glass Products
4.1 Material Selection
Prioritize borosilicate or tempered glass for cooking. Avoid soda-lime for hot beverages.

4.2 Certification Check
Look for GB4806.5-2016 or ASTM International certifications ensuring food safety.
5. Safe Usage Guidelines
5.1 Microwave Tips
Vent containers, add moisture to dry foods, remove all metal components.
5.2 Freezing Practices
Leave 1-2cm headspace to accommodate liquid expansion during freezing.
6. Glass Type Comparison Table
| Property | Soda-Lime | Tempered | Borosilicate | Crystal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Low | High | Very High | Low |
| Cost | $ | $$ | $$$ | $$$ |
| Best Use | Cold Storage | Oven/Microwave | Labs/Cooking | Decorative |

7. Alternatives to Glass
- Stainless Steel: Oven-safe but microwave-incompatible
- Silicone: Flexible but odor-prone
- Ceramic: Oven-friendly but fragile

8. Key Takeaways
- Choose borosilicate or tempered glass for thermal safety
- Verify GB4806.5-2016 certification
- Never heat sealed containers or use metal in microwaves