In the wake of a tragic accident involving a Xiaomi SU7, the world is abuzz with discussions about the safety of intelligent driving systems. This incident, which resulted in the loss of three lives, has not only sent shockwaves through the automotive industry but also highlighted critical issues surrounding the use and promotion of driving assistance technologies. As we delve into the details, it becomes evident that understanding how to use these systems correctly is paramount to preventing future tragedies.

Overview of the Accident
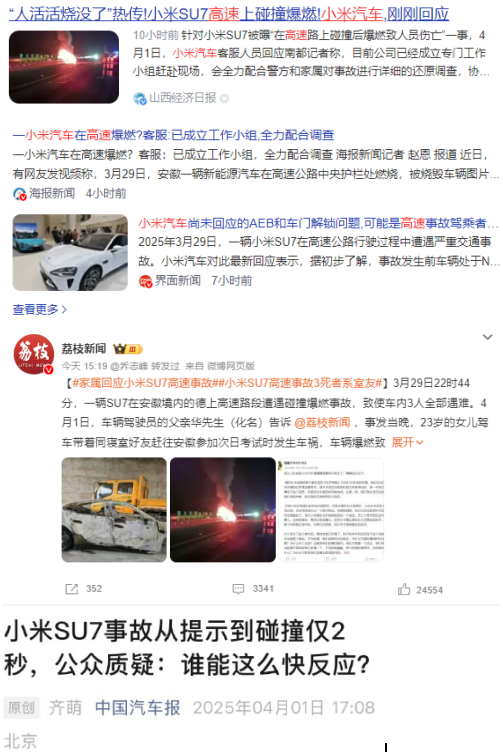
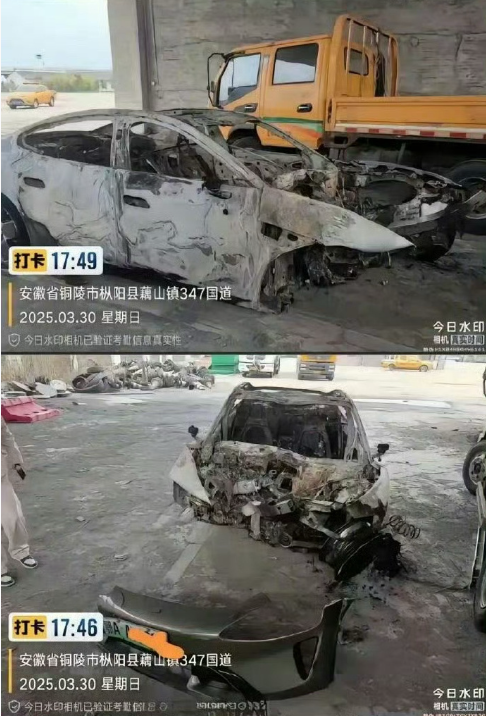
A serious traffic accident involving a Xiaomi SU7 car recently went viral on social media, causing Xiaomi’s stock price to fall by about 11 billion US dollars (about 80 billion yuan) in half a day. The accident killed all three people in the car, which was using an intelligent driving system to travel on the highway.
The Two Sides’ Versions of the Accident
The families of the victims were understandably questioning the situation due to the limited information available. However, the official statement released by Xiaomi triggered an even greater public relations crisis. This statement has become a negative example in the field of public relations, directly leading to the rapid spread of negative public opinion.

Analysis of the Problems with Xiaomi’s Public Relations Statement
Xiaomi’s official statement may seem professional and comprehensive, but there are several key problems:
- The target audience is not clear: The statement is too long and difficult for the general public to understand, while professionals can see the bias in it.
- Inappropriate way of presenting information: The long technical statement seems cold and lacking in empathy in the face of the family’s short and powerful questions.
- Clear shirking of responsibility: The statement gives the impression of blaming the victim entirely, which arouses public resentment.
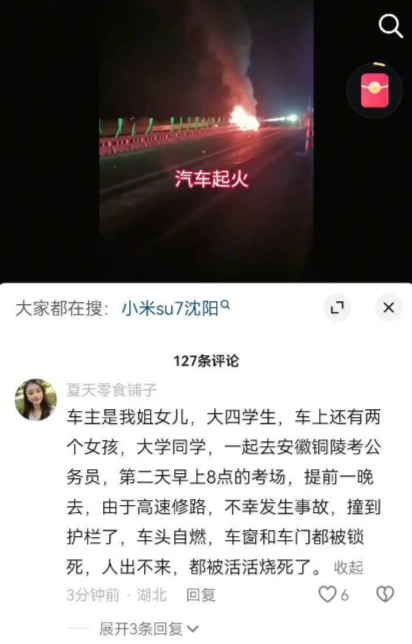
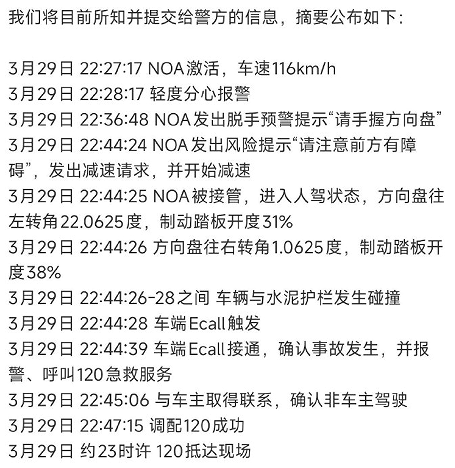
Restoring the True Course of the Accident
According to reliable information, the actual course of the accident was as follows:
- While the vehicle was traveling at 116 km/h, the system detected an abnormal road condition ahead and began to slow down, prompting the driver to take over.
- After taking over, the driver lightly applied the brakes and attempted to negotiate the curve at a speed of about 100 km/h.
- The vehicle crashed into a concrete wall at 97 km/h, resulting in the tragedy.
Expert analysis indicates that the outcome may have been different if the driver had chosen one of the following three options:
- Not taking over control at all, and letting the system do all the braking
- Taking over control and doing all the braking
- Passing the curve at a lower speed

Analysis of Xiaomi’s Responsibility
Xiaomi is indeed responsible for this accident, mainly in the following ways:
- Vague publicity of the intelligent driving function: making consumers have high expectations of the system’s capabilities.
- Lack of a clear description of the system’s capabilities: not clearly informing consumers of the situations in which manual intervention is required by the system.
Current Status of the Chinese Intelligent Driving Market
The Chinese intelligent driving market presents the following characteristics:
- Standards are too broad: The scope of capabilities included in Level 2 intelligent driving varies greatly, and everything from basic to advanced functions can be called Level 2.
- Varying capabilities of manufacturers: Intelligent driving systems from different manufacturers differ significantly in terms of algorithms, databases, and hardware configurations.
- Consumer perception bias: Some consumers regard the intelligent driving performance of leading companies such as Huawei as the industry’s general level.
Challenges Facing Intelligent Driving Technology
Even the most advanced intelligent driving systems have limitations:
- Unable to handle all road conditions: For example, construction curves such as those in this accident remain a challenge for many systems.
- Continuously evolving: The processing power of the same system may improve significantly at different times.
- Hardware configuration affects performance: The presence or absence of configurations such as lidar will directly affect system performance.
Safety Advice for Consumers
To ensure driving safety, consumers are advised to take the following measures:
- Urban area testing method: Newly purchased vehicles should be used in urban areas with intelligent driving for at least 3 months to confirm that there have been no accidents before considering high-speed use.
- Correct understanding of system capabilities: Clearly distinguish between the functional boundaries of “assisted driving” and “fully automated driving”.
- Maintain concentration: Even when using intelligent driving, the driver should always be prepared to take over.
- Understand system limitations: The intelligent driving capabilities of different models and configurations vary.
Suggestions for Industry Development
In order to promote the healthy development of the intelligent driving industry, it is recommended that:
- Refine industry standards: Establish more detailed classification standards within the L2 level.
- Strengthen consumer education: Help the public establish reasonable expectations.
- Improve testing standards: Establish a unified evaluation system for intelligent driving systems.
Intelligent driving technology is still developing, and consumers should maintain a rational understanding of it. They should neither over-rely on it nor reject it completely, but instead enjoy the convenience of technology while ensuring driving safety.